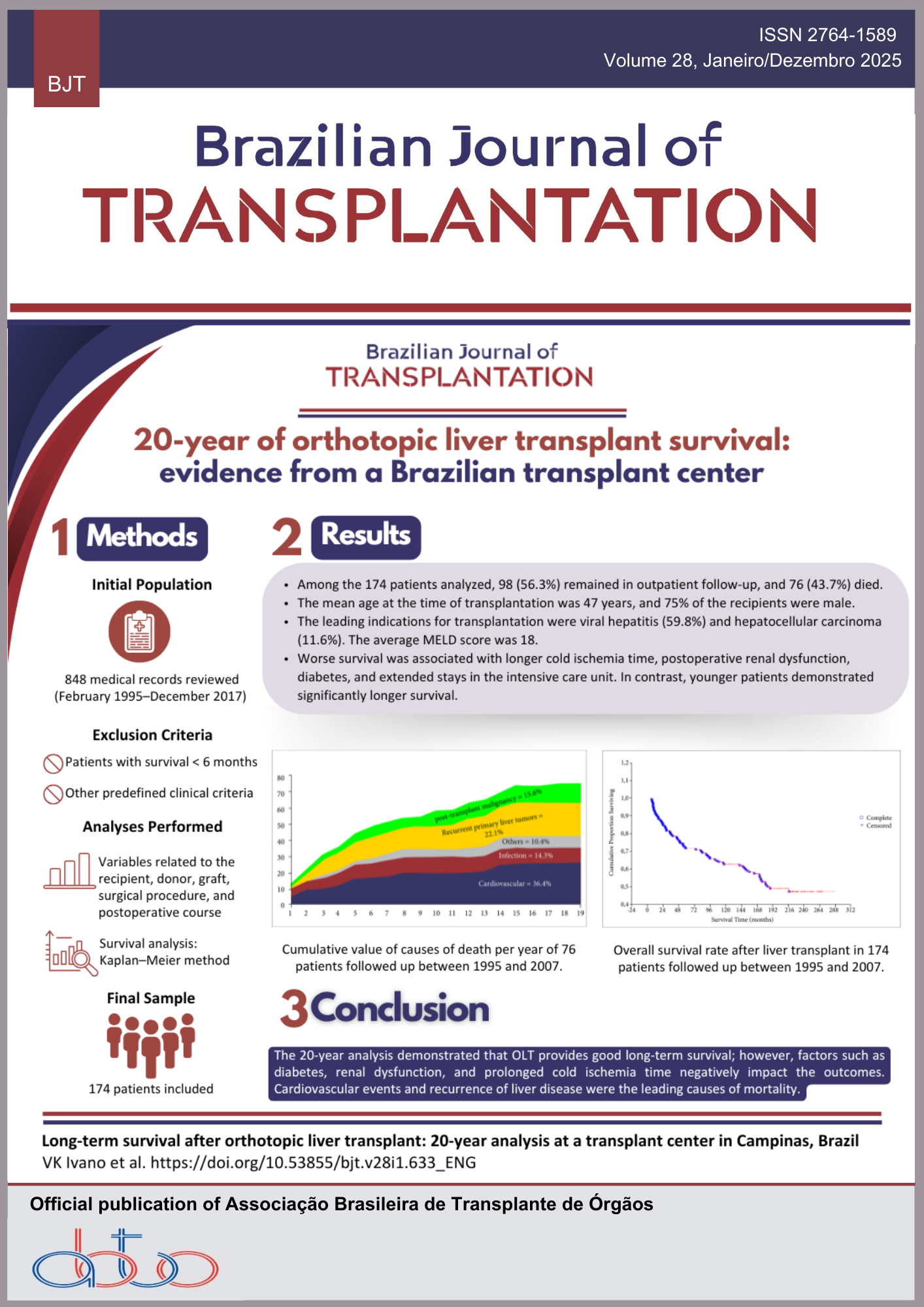
The Immune Response as a Model of (Really?) Random Natural Selection
Abstract
The natural selection analogy for the immune response is sophisticated. While the maturation of B lymphocytes resembles “survival of the fittest,” the formation of memory T lymphocytes prioritizes clonal diversity, which is crucial for fighting mutant pathogens. By reducing the TCR signal and the antigen affinity, the development of these memory cells can be accelerated. Thus, the immune strategy for long-term protection is diversity.
Downloads
References
1. Neumann J. The immune response as a model of random natural selection, from Charles Darwin to Susumo Tonegawa: a (provocative) text for non-immunologists. Braz J Transplant, 2025; 28(1): e2325. https://doi.org/10.53855/bjt.v28i1.684_ENG
2. Solouki S, Huang W, Elmore J, Limper C, Huang F, August A. TCR signal strength and antigen affinity regulate CD8+ memory T cells. J Immunol, 2020; 205(5):1217-27. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1901167
3. Kavazović I, Han H, Balzaretti G, Slinger E, Lemmermann NAW, ten Brinke A, et al. Eomes broadens the scope of CD8 T-cell memory by inhibiting apoptosis in cells of low affinity. PLoS Biol, 2020; 18(3): e3000648. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3000648
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Amanda de Menezes Mayer, José Artur Bogo Chies

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.