Time-Zero Biopsies in Deceased-Donor Kidney Transplantation: Predictive Value of Histological Findings on Long-Term Graft Function
Keywords:
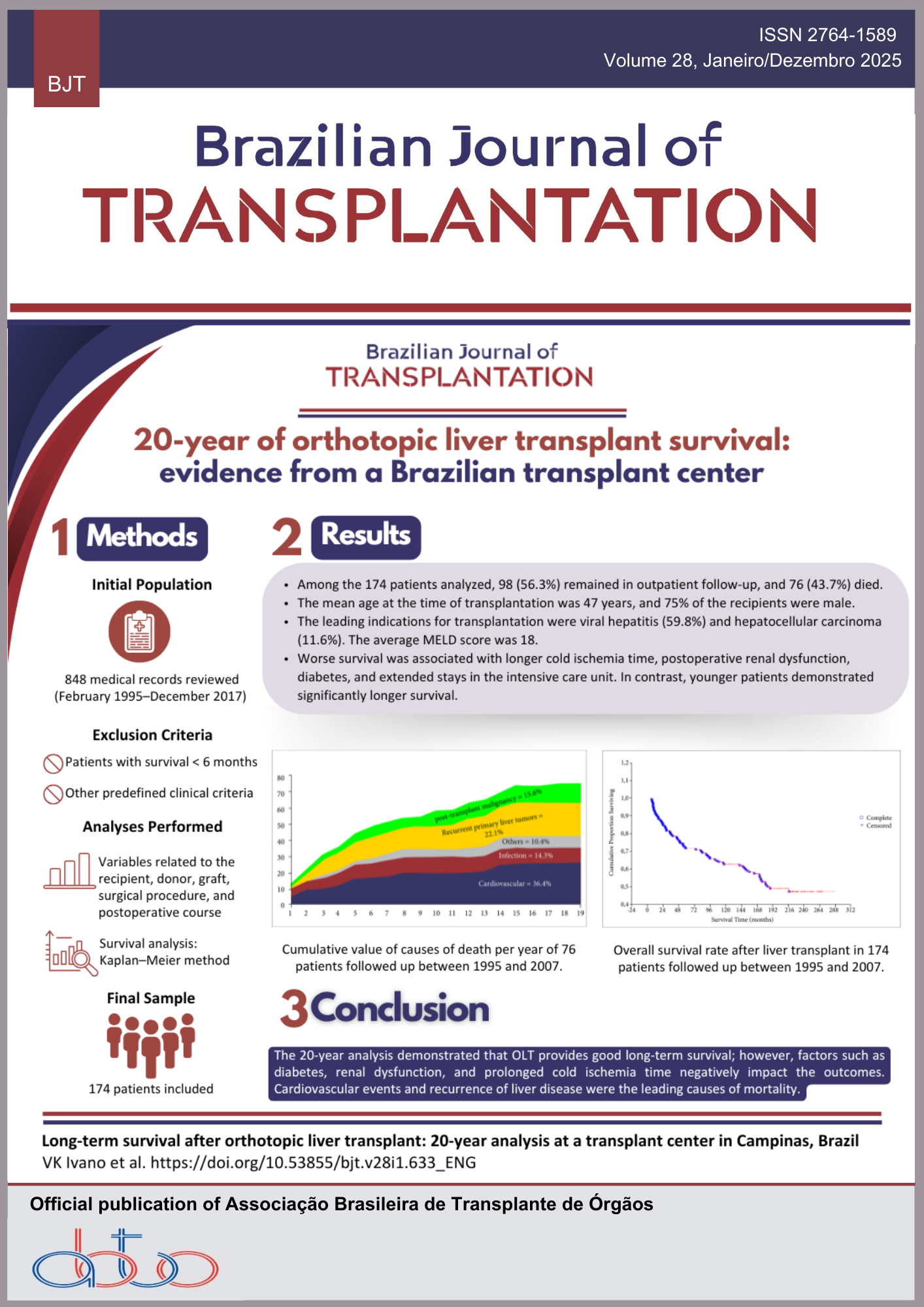
Renal TransplantationAbstract
Background: Time-zero biopsies (TzB) provide insights into donor-derived lesions, but their predictive value for long-term outcomes remains uncertain. We aimed to identify clinical and histological factors from TzB of deceased donors influencing glomerular filtration rate (GFR) at 3- and 5-year post-transplantation. Methods: We retrospectively analyzed TzB performed from January 2015 to August 2019. Nineteen biopsies were excluded due to recipient death before 3 years. We examined donor and recipient-related characteristics and histological findings categorized using the Banff scoring system. Results: Among 147 biopsies, 61.9% of donors were male, with a mean age of 51.8 ± 13.5 years, and 27.2% met expanded criteria. Histologic analysis revealed 44.2% had alterations in the Banff chronic scoring system: 29.1% in vascular fibrous intimal thickening (Cv), 26.6% in arteriolar hyalinosis (Ah), and 8.3% in interstitial fibrosis (Ci)/tubular atrophy (Ct). Mean GFR was 54.8 ± 21.2 and 52.3 ± 23.0 mL/min/1.73 m2 at 3 and 5 years, respectively. At 3 years, Ah > 0, Ci/Ct > 0, Cv > 0, Banff chronic sum score > 0, glomerulosclerosis (GE), donor age > 50 years, expanded criteria donors, and rejection episodes were significantly associated with lower GFR. With the exception of Ci/Ct, all other parameters were also significantly associated with lower GFR at 5 years. Linear regression indicated donor age [β (95%CI) = -0.257 (-0.783, -0.021); p = 0.039] and arteriolar hyalinosis [β (95%CI) = -0.207 (-16.767, -0.448); p = 0.039]; p = 0.039) as predictors of GFR at 3 years, with donor age maintaining predictive value at 5 years [β (95%CI) = -0.276 (-0.776, -0.137); p = 0.006]. A tendency towards predictive value for GFR at 5 years was noted for GE [β (95%CI) = -0.198 (120.0, 1.038); p = 0.054]. Conclusion: TzB provide valuable prognostic information for long-term graft function with histological findings (particularly arteriolar hyalinosis and GE) and donor age serving as significant predictors of GFR at 3 and 5 years post-transplantation. These findings suggest TzB can be useful for risk stratification and personalized management of KT recipients.
Downloads
References
Lodhi SA, Lamb KE, Meier-Kriesche HU. Solid organ allograft survival improvement in the United States: the long-term does not mirror the dramatic short-term success. Am J Transplant. 2011; 11(6): 1226-35. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-6143.2011.03539.x
Wolfe RA, Ashby VB, Milford EL, Ojo AO, Ettenger RE, Agodoa LY, et al. Comparison of mortality in all patients on dialysis, patients on dialysis awaiting transplantation, and recipients of a first cadaveric transplant. N Engl J Med. 1999; 341(23): 1725-30. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199912023412303
Gonçalves JA, Jorge C, Atalaia A, Matias P, Bruges M, Birne R, et al. New law of renal transplantation in Portugal associated with more acute rejection episodes and higher costs. Transplant Proc. 2012; 44(8): 2276-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.transproceed.2012.07.060
Reese PP, Aubert O, Naesens M, Huang E, Potluri V, Kuypers D, et al. Assessment of the utility of kidney histology as a basis for discarding organs in the United States: a comparison of international transplant practices and outcomes. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2021; 32(2): 397-409. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2020040464
Wang CJ, Wetmore JB, Crary GS, Kasiske BL. The donor kidney biopsy and its implications in predicting graft outcomes: a systematic review. Am J Transplant. 2015; 15(7): 1903-14. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajt.13213
Baylis C, Corman B. The aging kidney: insights from experimental studies. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1998; 9(4): 699-709. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.V94699
Epstein M. Aging and the kidney. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1996; 7(8): 1106-22. https://doi.org/10.1681/asn.v781106
Hiramitsu T, Tomosugi T, Futamura K, Okada M, Matsuoka Y, Goto N, et al. Adult living-donor kidney transplantation, donor age, and donor-recipient age. Kidney Int Rep. 2021; 6(12): 3026-34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ekir.2021.10.002
Veroux M, Grosso G, Corona D, Mistretta A, Giaquinta A, Giuffrida G, et al. Age is an important predictor of kidney transplantation outcome. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2012; 27(4): 1663-71. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfr524
Gaber LW, Moore LW, Alloway RR, Amiri MH, Vera SR, Gaber AO. Glomerulosclerosis as a determinant of posttransplant function of older donor renal allografts. Transplantation. 1995; 60(4): 334-9. Disponível em: https://journals.lww.com/transplantjournal/abstract/1995/08270/Glomerulosclerosis_As_A_Determinant_of.6.aspx
Bosmans JL, Woestenburg A, Ysebaert DK, Chapelle T, Helbert MJ, Corthouts R, et al. Fibrous intimal thickening at implantation as a risk factor for the outcome of cadaveric renal allografts. Transplantation. 2000; 69(11): 2388-94. Available from: https://journals.lww.com/transplantjournal/fulltext/2000/06150/fibrous_intimal_thickening_at_implantation_as_a.30.aspx
Gomes Filho FF, de Andrade LGM, Amaro JL, Barreti P, Yamamoto HA, Guerra R, et al. Impact of time zero biopsy on the outcome of transplanted kidneys. Transplant Proc. 2021; 53(10): 2895-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.transproceed.2021.09.016
Ibernon M, González-Segura C, Moreso F, Gomà M, Serón D, Fulladosa X, et al. Donor structural and functional parameters are independent predictors of renal function at 3 months. Transplant Proc. 2007; 39(7): 2095-8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.transproceed.2007.06.026
Lee AL, Huh KH, Lee SH, Lee JJ, Joo DJ, Jeong HJ, et al. Significance of time-zero biopsy for graft renal function after deceased donor kidney transplantation. Transplant Proc. 2016; 48(8): 2656-62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.transproceed.2016.07.020
Lee AL, Kim YS, Lim BJ, Jeong HJ, Joo DJ, Kim MS, et al. The impact of time-zero biopsy on early graft outcomes after living donor kidney transplantation. Transplant Proc. 2013; 45(8): 2937-40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.transproceed.2013.08.081
Raza SS, Agarwal G, Anderson D, Deierhoi M, Fatima H, Hanaway M, et al. Abnormal time-zero histology is predictive of kidney transplant outcomes. Clin Transplant. 2022; 36(7): e14676. https://doi.org/10.1111/ctr.14676
Munivenkatappa RB, Schweitzer EJ, Papadimitriou JC, Drachenberg CB, Thom KA, Perencevich EN, et al. The Maryland Aggregate Pathology Index: a deceased donor kidney biopsy scoring system for predicting graft failure. Am J Transplant. 2008; 8(11): 2316-24. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-6143.2008.02370.x
Taub HC, Greenstein SM, Lerner SE, Schechner R, Tellis VA. Reassessment of the value of post vascularization biopsy performed at renal transplantation: the effects of arteriosclerosis. J Urol. 1994;151(3): 575-7. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-5347(17)35018-8
Cockfield SM, Moore RB, Todd G, Solez K, Gourishankar S. The prognostic utility of deceased donor implantation biopsy in determining function and graft survival after kidney transplantation. Transplantation. 2010; 89(5): 559-66. https://doi.org/10.1097/TP.0b013e3181ca7e9b
Randhawa PS, Minervini MI, Lombardero M, Duquesnoy R, Fung J, Shapiro R, et al. Biopsy of marginal donor kidneys: correlation of histologic findings with graft dysfunction. Transplantation. 2000; 69(7): 1352-7. Available from: https://journals.lww.com/transplantjournal/fulltext/2000/04150/_SUBOPTIMAL__KIDNEY_DONORS__The_Experience_with.24.aspx
Roufosse C, Naesens M, Haas M, Lefaucheur C, Mannon RB, Afrouzian M, et al. The Banff 2022 Kidney Meeting Work Plan: data-driven refinement of the Banff Classification for Renal Allografts. Am J Transplant. 2024; 24(3): 350-61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajt.2023.10.031
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Bárbara Beirão, Henrique Borges, Joana Trigo Medeiros , Filipa Fonte Rodrigues , Ana Pena, Mário Góis, Helena Viana, Cristina Jorge

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.