Liver Changes Caused by Sars-CoV-2
Keywords:
SARS-CoV2, COVID-19, Hepatocytes, Pandemics, Cytokine Release Syndrome, Hepatic Cirrhosis, HypoxiaAbstract
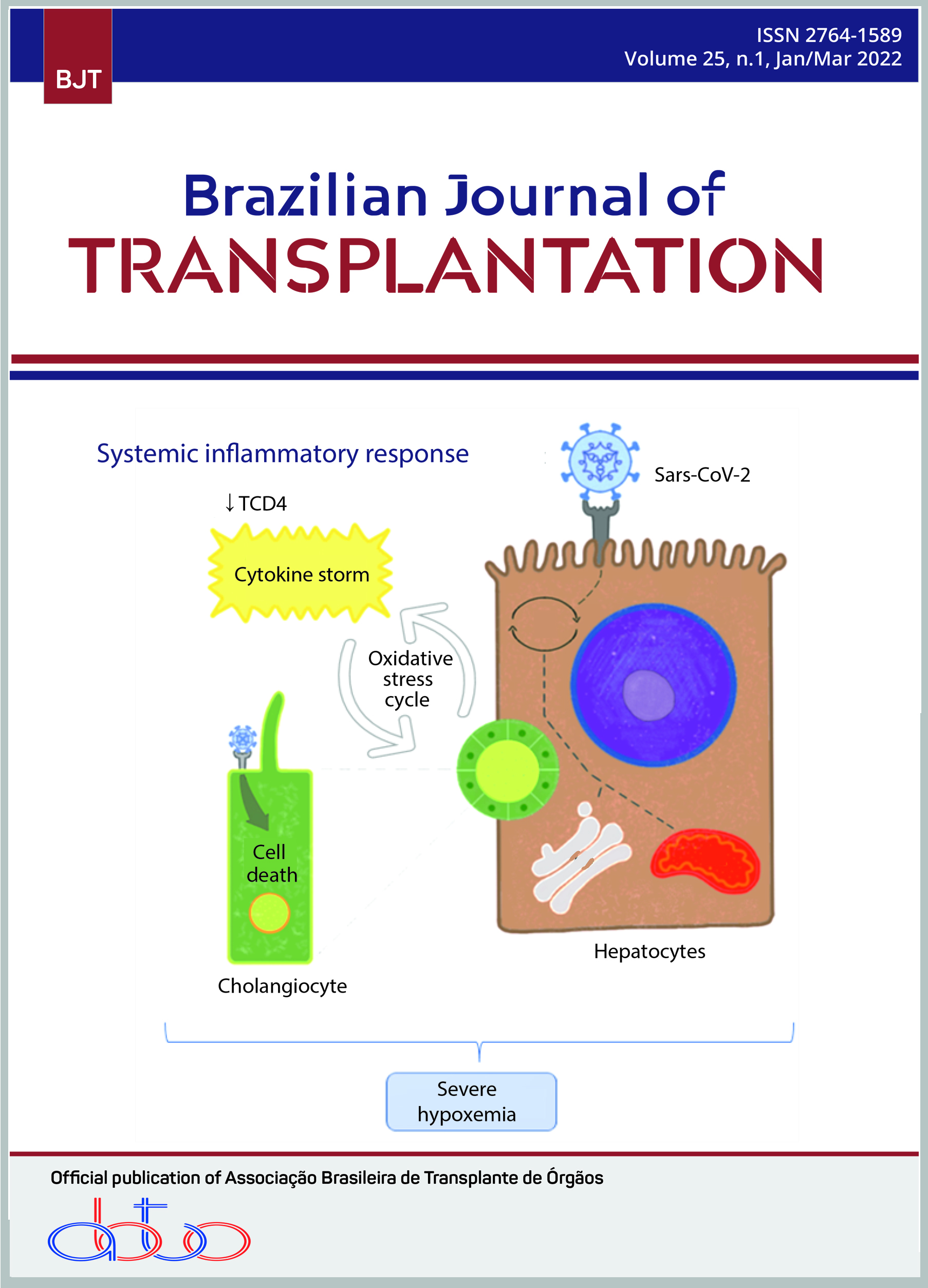
With the Sars-CoV-2 virus endemic, many individuals with preexisting liver diseases such as liver cirrhosis and chronic liver diseases have become exposed to decompensation due to the virulence of exposure and individual susceptibility to the new coronavirus infection. The direct cytotoxicity of the Sars-CoV-2 virus occurs through its replication in liver cells, given by the binding of the agent to the target cells by the expression of the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), which is the main mediator of viral replication in infected patients. by Covid-19. As a consequence, proinflammatory cytokines increase and can cause hypoxia and systemic ischemia. In association with lymphopenia and a decrease in CD4+ T-cell levels, patients may progress to decompensation or worsening of the infectious condition, with chronic liver failure worsening since the first week and, thus, a decrease in survival. Patients pre-diagnosed with cirrhosis and infected with the Covid-19 virus have greater liver involvement and worse prognosis and, therefore, deserve special monitoring, being carefully evaluated in order to enable the reduction of liver damage caused by the infection.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Fidel Benaia Moro do Nascimento, Artur Kiesqui Zattar, Matthew Silvestre de Castro, Gabriela Miranda Fabris, Vitória Carolina Bitencourt da Silva, Maria Eduarda Costa Oliveira, Lucas de Oliveira Rodrigues, Marina Zanatta Pessoa de Lima, Rafaela Buri, Fernanda Gonçalves Souza, Victor Nogueira de Jesus, Vitória Silveira da Silva

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.