Factors related to the non-authorization of organ and tissue donation by the families who refused organ donation
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.53855/bjt.v24i4.429Abstract
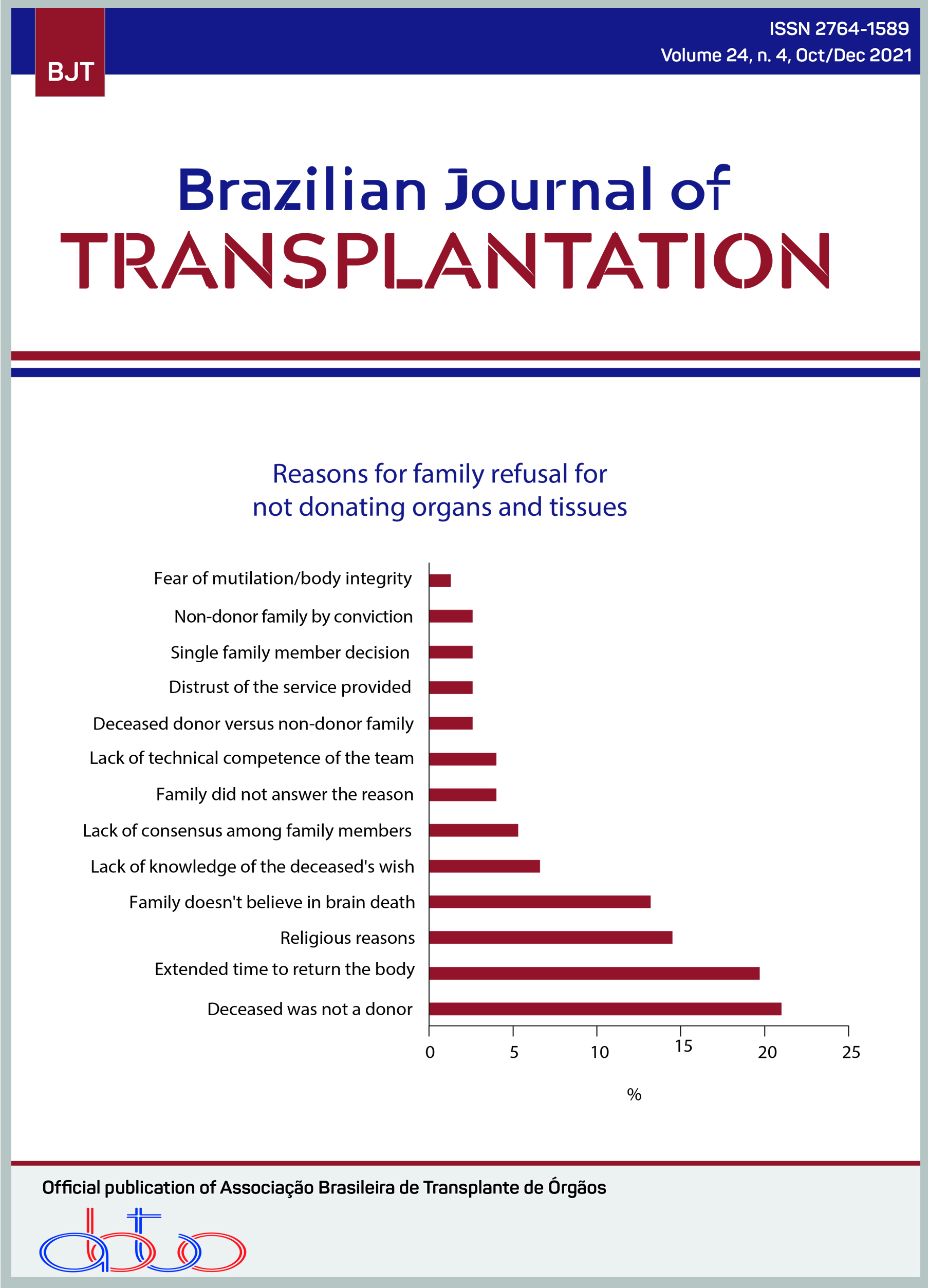
Purpose: To characterize the care provided to potential donors eligible for donation and their families, and to understand why family members refuse organ and tissue donation. Method: Quantitative, descriptive, exploratory, and retrospective study, with 76 potential donors notified in 2015, whose donation was not carried out due to family refusal. Data was obtained from medical records of the Organ Search Organization at Hospital de Clínicas from Unicamp, and submitted to descriptive analysis. Results: There was a predominance of white individuals (75%), male (61.8%), with ages between 20 and 60 years (78.9%), married (42.1%), hospitalized in the vicinity of Campinas (47.4%), affected by stroke (56.6%) and assisted in intensive care units (77.7%). The length of hospital stays until the diagnosis of brain death ranged from one to 29 days. In 87.4% of cases brain death was explained to family members up to 12 hours after death. As to the interviews, 78.4% of families were interviewed immediately after the clarification of brain death; only 65.2% of these were performed in private environments; 57.9% by professionals working in the donation; 43.4% to a first-degree relative. Among the reasons for not donating, the following prevailed: the deceased was not a donor (21%), extended time to return the body for burial (19.7%), religious reasons (14.5%), and family members who do not believe in death brain (13.2%). Conclusion: It was verified predominance of PD in intensive care beds, but there are still many kept in emergency rooms, communication of the brain death performed in non-private environments, and made by non-capable professionals, and these influenced the incidence of non-doors.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2021 Simey de Lima Lopes Rodrigues, Ilka de Fatima Santana Ferreira Boin, Helder Jose Lessa Zambelli, Luiz Antônio da Costa Sardinha, Elaine Cristina Ataíde, Marli Elisa Nascimento Fernandes

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.